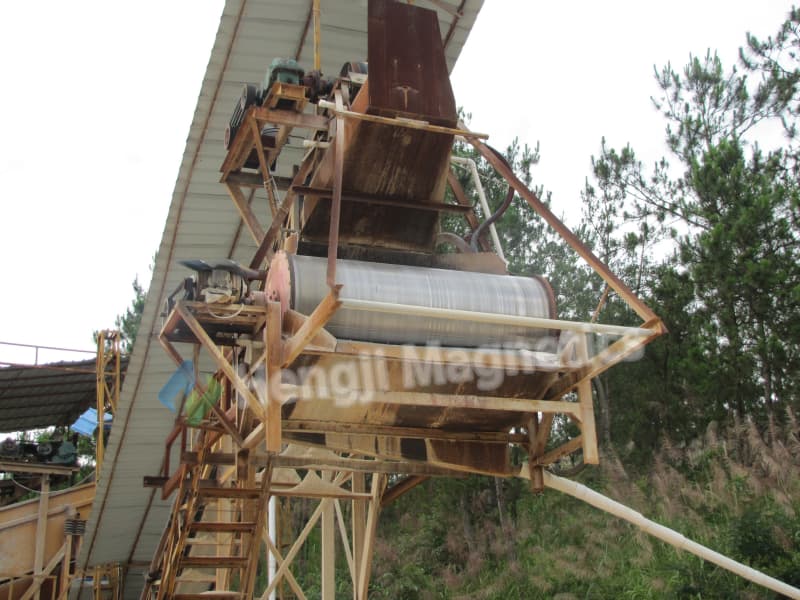
Selecting the right equipment for your mine or quarry is more than just matching a model number to your belt width. The technical specifications on a datasheet are vital starting points, but they are static numbers. The true measure of a powerful iron magnetic separator lies in understanding the dynamic magnetic performance under your specific working conditions. This guide will help you interpret key specs and the underlying principles, like the magnetic force curve, to accurately predict how a mining magnetic separator will perform on your site, ensuring you invest in a solution that delivers reliable, long-term protection.

Decoding the Datasheet: Key Parameters Explained
Let’s break down the most critical numbers you’ll encounter when evaluating a mining magnetic separator.
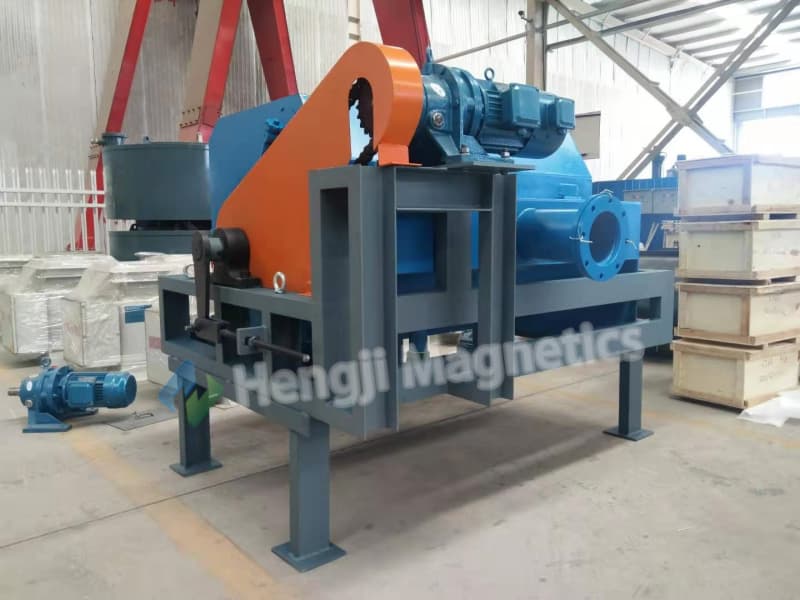 1. Magnetic Strength Rating (e.g., T1, T2, T3):
1. Magnetic Strength Rating (e.g., T1, T2, T3):
This is the engine power of your iron magnetic separator. A higher “T” rating indicates a stronger, deeper magnetic field.
-
What it means: A T3-rated separator generates a more intense field than a T2 or T1 model of the same size. This translates directly to a greater ability to lift heavier tramp metal and to pull contaminants from deeper within the material burden on your conveyor.
2. Maximum Burden Depth & Lift Capacity:
These related specs tell you about the separator’s reach and power.
-
Burden Depth: This indicates how thick a layer of material the magnetic field can effectively penetrate. A true heavy-duty mining magnetic separator is designed for deep burdens common in raw ore handling.
-
Lift Capacity (e.g., 0.1–35 kg): This range shows the weight of a single ferrous object the separator can capture under ideal conditions. Remember, a long, flat piece of steel plate requires more magnetic “grip” than a dense, compact object of the same weight.
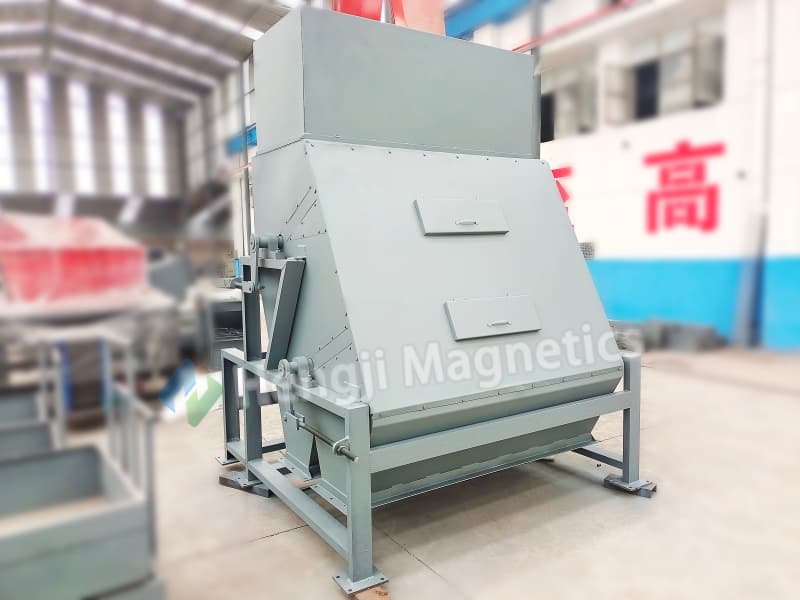 3. Cooling System Type (Air-Cooled, Oil-Cooled):
3. Cooling System Type (Air-Cooled, Oil-Cooled):
This spec defines duty cycle and environmental ruggedness.
-
Air-Cooled: Efficient and lower maintenance, suitable for most standard applications.
-
Oil-Cooled: Offers superior, sealed cooling for the toughest environments—high ambient heat, extreme dust, and 24/7 continuous operation. This ensures a mining magnetic separator maintains stable magnetic performance without overheating.
Understanding the Magnetic Force Curve: The Key to Real Performance
The most crucial concept not shown on a simple datasheet is the magnetic force curve. Magnetic strength does not drop linearly; it decays rapidly with distance.
-
The Principle: The power of an iron magnetic separator at the magnet’s surface is immense, but it weakens significantly just a few centimeters away. This is why the installation “suspension height” above the belt is so critical.
-
Real-World Translation: A separator rated to lift a 25kg ball at 400mm might struggle with a 10kg plate at 500mm. You must always consider the actual distance between the magnet and the deepest tramp metal in your material stream. Choosing a unit with performance headroom (a higher T-rating) accounts for this decay and ensures reliable operation.
Your Pre-Purchase Checklist for a Mining Magnetic Separator
Use this framework to move from specs to guaranteed performance:
-
Audit Your Site Conditions: Measure your exact belt width, maximum material burden depth, and tramp metal size/shape. Note environmental factors like dust, heat, and moisture.
-
Match the Magnet to the Burden: Select a mining magnetic separator whose rated burden depth and magnetic strength (T-rating) exceed your maximums. This built-in safety margin is essential for handling peak loads and irregular material flow.
-
Plan for Proper Installation: Ensure you can install the iron magnetic separator at the optimal, low height recommended by the manufacturer to maximize magnetic force on the belt.
-
Choose the Right Configuration: For automated operation, select a self-cleaning model. For hazardous areas, specify an explosion-proof unit. Match the cooling system to your operational tempo and environment.
Conclusion: Invest in Understanding, Not Just a Product
A powerful mining magnetic separator is a long-term investment in plant safety and efficiency. By looking beyond the basic specifications to understand magnetic force curves and applying them to your unique conditions, you make an informed, confident choice. The right iron magnetic separator won’t just meet a spec sheet—it will consistently protect your crushers, screens, and process flow from damaging tramp metal, year after year. Don’t just buy a magnet; invest in a solution engineered for your reality.



 Categories
Categories